If you’ve ever wondered whether concurrency and parallelism are the same thing — you’re not alone. In modern programming, the terms concurrency and parallelism are often used interchangeably — but they are not the same. Understanding their differences is crucial for building efficient, scalable, and high-performance software.
In this guide, we’ll explore both concepts through:
- Simple definitions
- Real-world analogies
- Beginner-friendly C# code examples
- Visual comparisons and use cases
🔄 What is Concurrency?
➤ Definition:
Concurrency is about managing multiple tasks at the same time. It doesn’t mean those tasks are running simultaneously; instead, the system interleaves their execution — often by switching between them very quickly.
This can be done even on a single core by scheduling tasks efficiently.
➤ How it works:
Think of a single-core processor as a skilled juggler. It can only handle one ball at a time, but it switches between them quickly enough that it seems like all the balls are in the air at once. That’s concurrency — not actually doing everything simultaneously, but making progress on multiple things.
🧠 Analogy:
Imagine you’re writing code while talking on the phone. You write a few lines, then respond to a question, then continue coding. You’re not doing both at once, but juggling them in a way that feels simultaneous.
✅ C# Example – Concurrency using async/await
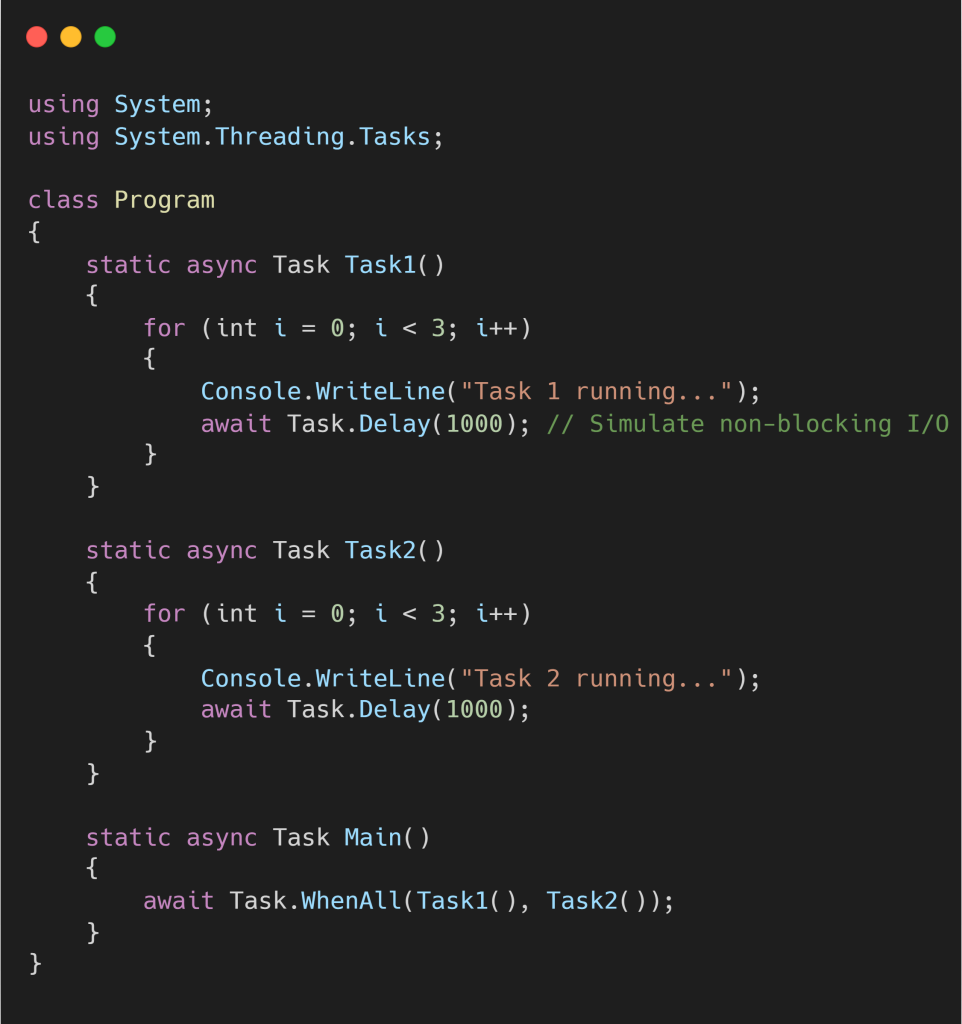
🔍 What happens here?
Even though there’s only one thread, both tasks take turns running when the other is awaiting. This is ideal for I/O-bound tasks (like reading files or calling APIs), where you don’t want the app to sit idle while waiting.
⚡ What is Parallelism?
➤ Definition:
Parallelism is about executing multiple tasks simultaneously, using multiple CPU cores or processors. Each task runs on a different core or thread at the same time.
➤ How it works:
Imagine you have a kitchen with four chefs, each working on a different part of the meal simultaneously. This is true parallelism — multiple tasks happening in parallel, with no switching needed.
🧠 Analogy:
You and three friends are working on different parts of a group project at the same time. Each of you has your own laptop. That’s parallelism — no one is waiting for anyone else to finish before starting their part.
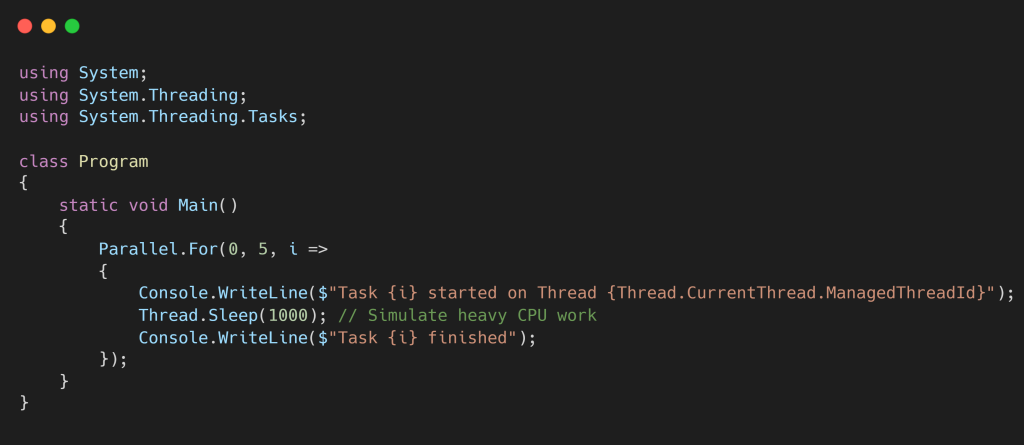
✅ C# Example – Parallelism using Parallel.For
✅ C# Example – Parallelism using Task.Run
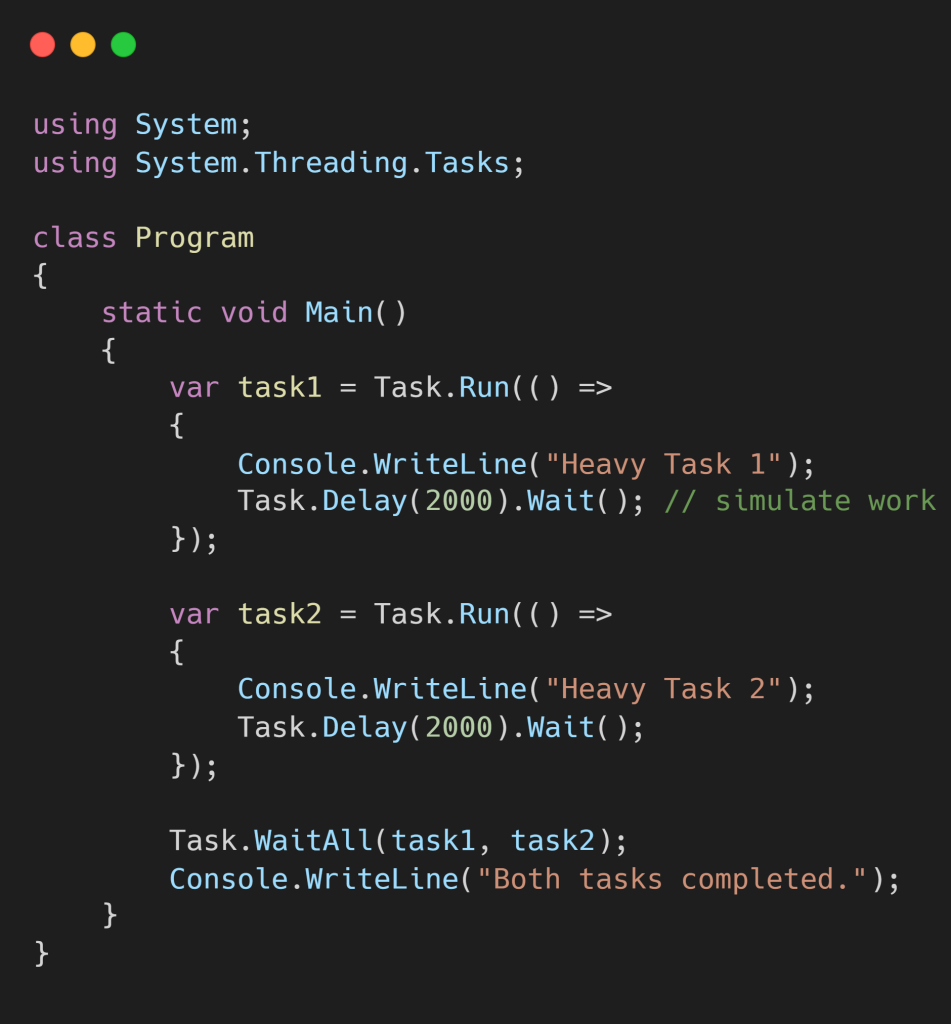
🔍 What happens here?
Each task runs on its own thread, potentially on different cores, allowing them to execute in true parallel — great for CPU-bound tasks like number crunching, data processing, or video encoding.
💡 Concurrency vs Parallelism: Side-by-Side
| Feature | Concurrency | Parallelism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manage multiple tasks efficiently | Execute multiple tasks simultaneously |
| Core Usage | Can work on a single core | Requires multiple cores/threads |
| Example | Async file reads, API calls | Video rendering, matrix computations |
| Ideal For | I/O-bound tasks | CPU-bound tasks |
| Language Tools | async/await, Task, Thread | Parallel.For, Task.Run, ThreadPool |
| Analogy | Switching between cooking and texting | Two people cooking different dishes at once |
🎯 Can You Use Both?
Absolutely. In many real-world systems, concurrency and parallelism work together.
Example: A web server:
- Uses concurrency to handle thousands of simultaneous requests efficiently.
- Uses parallelism to perform CPU-intensive tasks (like image processing) faster.
Think of it as:
The waiter handles multiple tables (concurrency), while multiple chefs cook meals in parallel (parallelism).
🛠️ Tips for Beginners
- Use
async/awaitfor non-blocking, I/O-heavy operations. - Use
Parallel.FororTask.Runfor CPU-heavy tasks that can be split. - Avoid shared mutable state unless using synchronization (
lock,Semaphore,ConcurrentCollection, etc.). - If multiple tasks access the same data, use synchronization to avoid race conditions.
- Don’t parallelize just for the sake of it — measure performance first.
🧪 Which Should You Use?
| Task | Use Concurrency | Use Parallelism |
|---|---|---|
| Calling external APIs | ✅ | 🚫 |
| Reading files from disk | ✅ | 🚫 |
| Compressing large files | 🚫 | ✅ |
| Machine learning training | 🚫 | ✅ |
| Real-time chat messaging | ✅ | 🚫 |
🔚 Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between concurrency and parallelism is a core skill for modern developers. Both are essential tools for development, but they solve different problems.
- Use concurrency to keep your app responsive and scalable.
- Use parallelism to speed up heavy computation by dividing the load across cores.
Whether you’re building responsive desktop apps, high-throughput APIs, or high-performance services — using both concepts wisely will make your software faster, leaner, and more efficient.


